Getting Started with Palo Alto Networks: Beginner’s Training Guide
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, Palo Alto Networks has emerged as a powerhouse, consistently leading the pack in network security innovation. Whether you're a fresh graduate or an IT professional looking to pivot into security, understanding how to navigate the Palo Alto ecosystem is a career-defining move.
This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap for getting started with Palo Alto Networks in 2026.
What is Palo Alto Networks?
Palo Alto Networks is a global leader in cybersecurity, best known for pioneering the Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW). Unlike traditional firewalls that only look at ports and protocols, Palo Alto's technology inspects traffic based on applications, users, and content.
Today, the company has expanded into a "three-platform" strategy:
- Strata: Next-Generation Firewalls (Hardware and Virtual).
- Prisma: Cloud-native security for hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Cortex: AI-driven security operations (SecOps) and endpoint protection.
Market Share of Palo Alto
As of 2025-2026, Palo Alto Networks maintains a dominant position in the cybersecurity market. They are frequently positioned as a "Leader" in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls.
Market Share Comparison
In the enterprise firewall market, Palo Alto typically holds a significant lead over competitors like Fortinet and Check Point.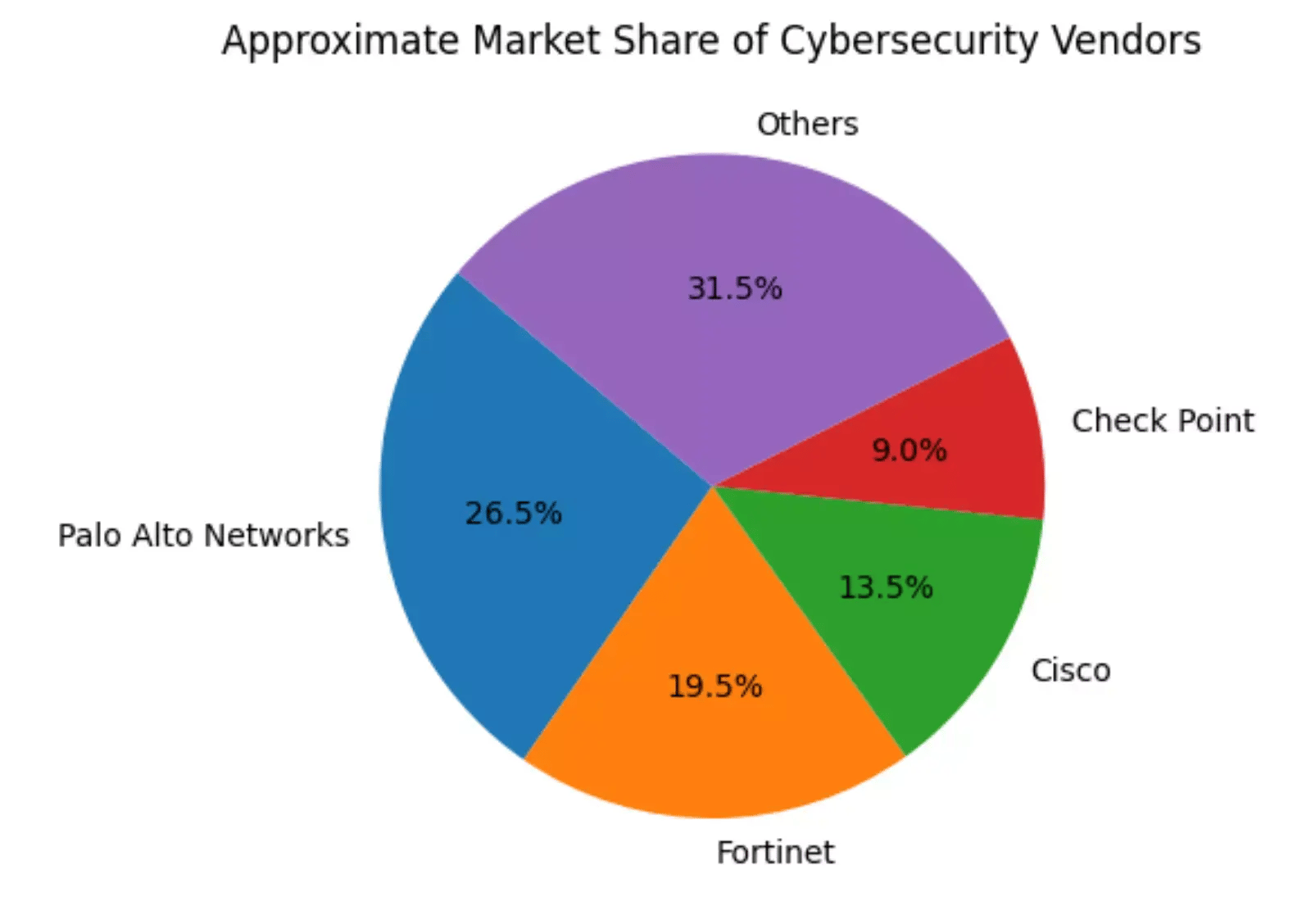
Why to Take Palo Alto Training?
- Industry Recognition: It is the "Gold Standard" for network security.
- AI Integration: You learn to work with Precision AI, which Palo Alto uses to automate threat detection.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Most modern enterprises are moving to Zero Trust; Palo Alto is the primary tool used to implement it.
- High Demand: There is a massive global shortage of skilled cybersecurity engineers who can manage these specific platforms.
Who Can Do Palo Alto Training?
- Students/Freshers: Those looking to enter the IT security domain.
- Network Engineers: Professionals managing routers/switches who want to move into security.
- System Administrators: Individuals responsible for overall IT infrastructure.
- Security Analysts: Those working in a SOC (Security Operations Center) environment.
Course Outcome
By completing a Palo Alto training program (like the PCNSA or PCNSE tracks), you will be able to:
- Install and configure Next-Generation Firewalls.
- Implement App-ID, User-ID, and Content-ID to secure traffic.
- Manage multiple firewalls centrally using Panorama.
- Configure site-to-site VPNs and remote access (GlobalProtect).
- Understand and deploy cloud security via Prisma Cloud.
Career Opportunities in Palo Alto
The certification opens doors to various high-level roles:
- Network Security Engineer
- Security Architect
- SOC Analyst (Level 2 or 3)
- Cloud Security Specialist
- Systems Engineer (Pre-sales)
Skills Required to Become a Palo Alto Professional
To succeed, you don't just need to know the "buttons" to click. You need a foundation in:
- Networking Fundamentals: Understanding OSI layers, TCP/IP, and routing/switching.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Understanding SSL/TLS decryption is critical.
- Cloud Literacy: Basic knowledge of AWS, Azure, or GCP.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to look at logs and identify patterns of an attack.
Salary Package: Experience vs. Package
Palo Alto certified professionals are among the highest-paid in the networking industry.
Salary Growth (USD per Annum)
| Experience Level | Average Salary Range (USD) |
| Entry-Level (0-2 years) | $75,000 - $95,000 |
| Mid-Level (3-6 years) | $105,000 - $140,000 |
| Senior/Architect (7+ years) | $155,000 - $210,000+ |
Companies Hiring Palo Alto Professionals
Almost every Fortune 100 company uses Palo Alto Networks. Major recruiters include:
- Tech Giants: Google, Amazon, Microsoft.
- Financial Institutions: JP Morgan Chase, Goldman Sachs, HSBC.
- Consultancies: Accenture, Deloitte, PwC, Wipro, TCS.
- Telecommunications: AT&T, Verizon, Cisco.
Roles and Responsibilities
In a typical day-to-day role, a Palo Alto professional will:
- Policy Management: Writing and auditing security rules to allow or block traffic.
- Threat Hunting: Monitoring logs in Cortex XDR to find hidden threats.
- Upgrades & Patching: Ensuring PAN-OS is updated to the latest secure version.
- VPN Management: Ensuring remote employees can connect securely via GlobalProtect.
- Troubleshooting: Using CLI and GUI tools to find why a specific application is failing.
Steps to Prepare for Palo Alto Certification
- Pick Your Path: Start with PCCET (Entry) or PCNSA (Administrator). Aim for PCNSE (Engineer) for expert status.
- Use Beacon: Palo Alto’s "Beacon" portal offers free digital learning modules.
- Build a Lab: Use Palo Alto VM-Series firewalls in a virtual lab (like EVE-NG or GNS3) to practice configuration.
- Review the Blueprint: Every exam has a "Domain Weightage" list—focus your study time accordingly.
- Practice Exams: Take official practice tests to get used to the scenario-based questions.
Conclusion
Getting certified in Palo Alto Networks isn't just about adding a line to your resume; it’s about mastering a platform that protects the world's most sensitive data. With the shift toward AI-driven security and cloud-native environments, these skills will only become more valuable in the years to come.
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Getting Started with Oracle Eloqua: A Beginner’s Guide

Learn Java Microservices from Scratch: Beginner’s Complete Guide


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think