Learn Java Microservices from Scratch: Beginner’s Complete Guide
In today's fast-paced digital world, businesses demand applications that are scalable, resilient, and easy to maintain. Monolithic applications, while once the standard, often struggle to meet these demands. This is where Java Microservices come into play, offering a revolutionary approach to software development. If you're looking to future-proof your career in software, understanding and mastering Java Microservices is a must.
What are Java Microservices?
Java Microservices represent an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled, independently deployable services. Instead of building a single, large application (a monolith), you break it down into smaller, self-contained services, each responsible for a specific business capability.
Imagine a large e-commerce website. In a monolithic architecture, everything from product catalog management to order processing and payment gateways would be part of a single codebase. With microservices, you might have separate services for:
- Product Catalog Service: Manages product information.
- Order Service: Handles order creation and tracking.
- Payment Service: Processes payments.
- User Service: Manages user accounts and profiles.
These services communicate with each other through lightweight mechanisms, often using REST APIs or message brokers. This modularity offers numerous benefits, which we'll explore shortly.
Market Share of Java Microservices
Java has long been a powerhouse in enterprise application development, and its adoption in the microservices landscape is no exception. While various languages can be used for microservices, Java, with its robust ecosystem, mature frameworks (like Spring Boot), and strong community support, remains a dominant player.
Here's a look at the estimated market share of technologies used for microservices development.
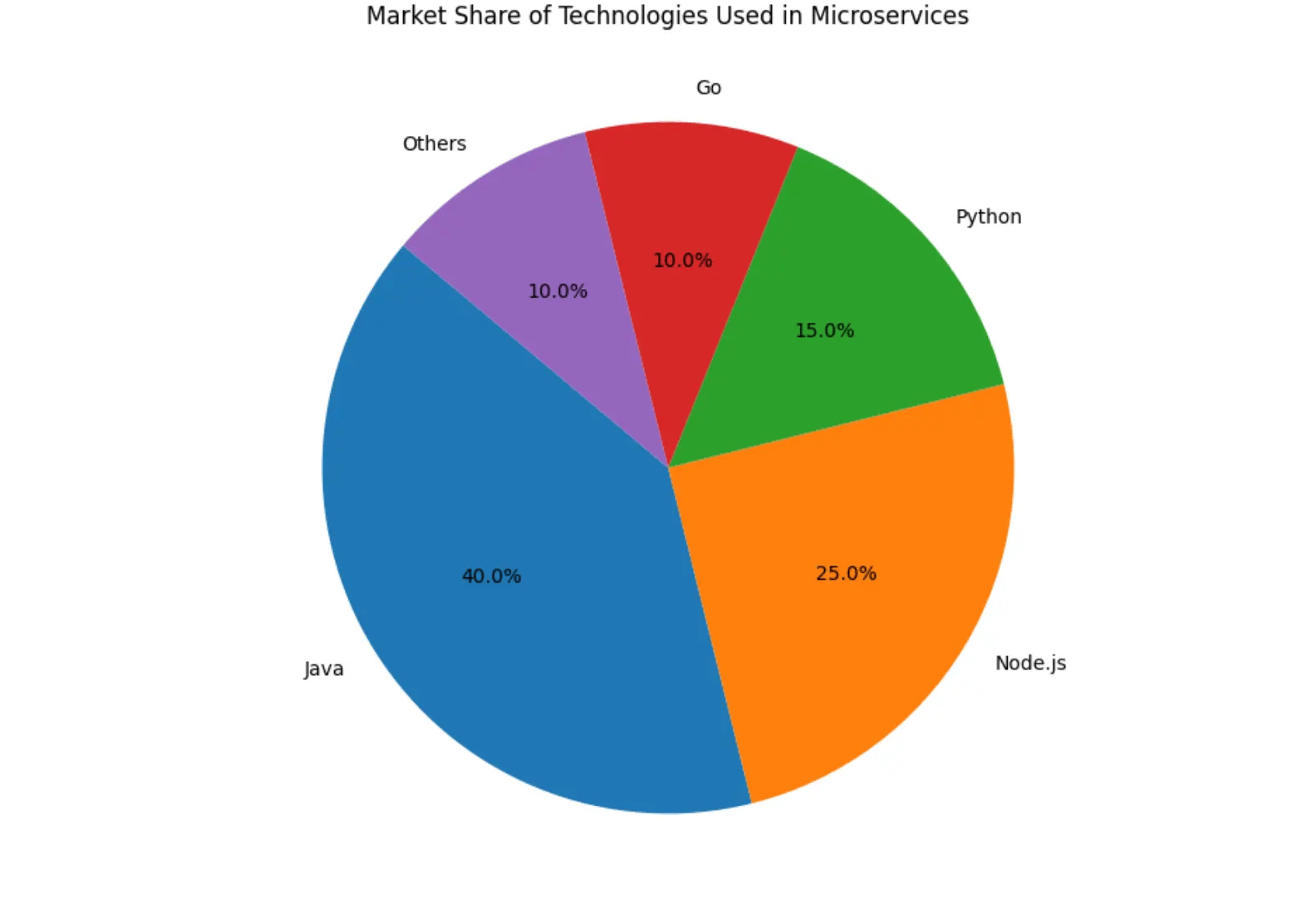
As you can see, Java holds a significant portion of the market, making it a highly valuable skill for any aspiring microservices developer.
Why to take Java Microservices Training
Investing in Java Microservices training is a strategic move for several compelling reasons:
- High Demand: The industry is actively seeking developers proficient in microservices, and Java developers with this expertise are particularly sought after.
- Scalability: Learn how to build applications that can handle millions of users and transactions by scaling individual services independently.
- Resilience: Understand how to design systems that can tolerate failures in individual services without bringing down the entire application.
- Faster Development Cycles: Microservices enable smaller, independent teams to work on different services concurrently, leading to quicker feature releases.
- Technology Agnostic: While you'll be focusing on Java, the principles of microservices are universal, allowing you to adapt to other technologies more easily.
- Career Advancement: This skill set positions you for senior developer, architect, and lead roles.
Who can do Java Microservices Training
Java Microservices training is ideal for a wide range of professionals, including:
- Experienced Java Developers: Those looking to modernize their skills and transition from monolithic to microservices architecture.
- Software Engineers: Developers from other programming backgrounds who want to leverage Java's robust ecosystem for microservices.
- Backend Developers: Anyone focused on server-side development seeking to build scalable and resilient systems.
- Architects: Professionals aiming to design and implement modern, distributed application architectures.
- DevOps Engineers: Understanding microservices is crucial for deploying, monitoring, and managing these distributed systems effectively.
- Freshers/Students: Ambitious beginners with a foundational understanding of Java who want to kickstart their careers in a high-demand field.
Course Outcome
Upon completing a comprehensive Java Microservices training program, you should be able to:
- Understand the core principles and benefits of microservices architecture.
- Design and develop RESTful APIs using Spring Boot.
- Implement service discovery, API gateways, and load balancing.
- Manage data consistency in a distributed environment.
- Implement authentication and authorization for microservices.
- Containerize microservices using Docker.
- Orchestrate and deploy microservices using Kubernetes (introductory level).
- Monitor and troubleshoot microservices applications.
- Apply best practices for building robust and scalable microservices.
Career Opportunities in Java Microservices
The demand for Java Microservices professionals is booming across various industries. Here are some of the exciting career paths you can pursue:
- Java Microservices Developer: Design, develop, and maintain individual microservices.
- Backend Developer (Java/Spring Boot): Focus on the server-side logic and API development using Java and Spring Boot.
- Cloud Engineer: Work with cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) to deploy and manage microservices.
- DevOps Engineer: Automate the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of microservices.
- Solution Architect: Design the overall architecture of microservices-based systems.
- Technical Lead: Guide teams in developing and implementing microservices solutions.
Salary Package
Salaries for Java Microservices professionals are highly competitive and generally increase significantly with experience and expertise. Here's a graphical representation of typical salary ranges based on experience in the United States (these figures can vary by location, company size, and specific skill set).
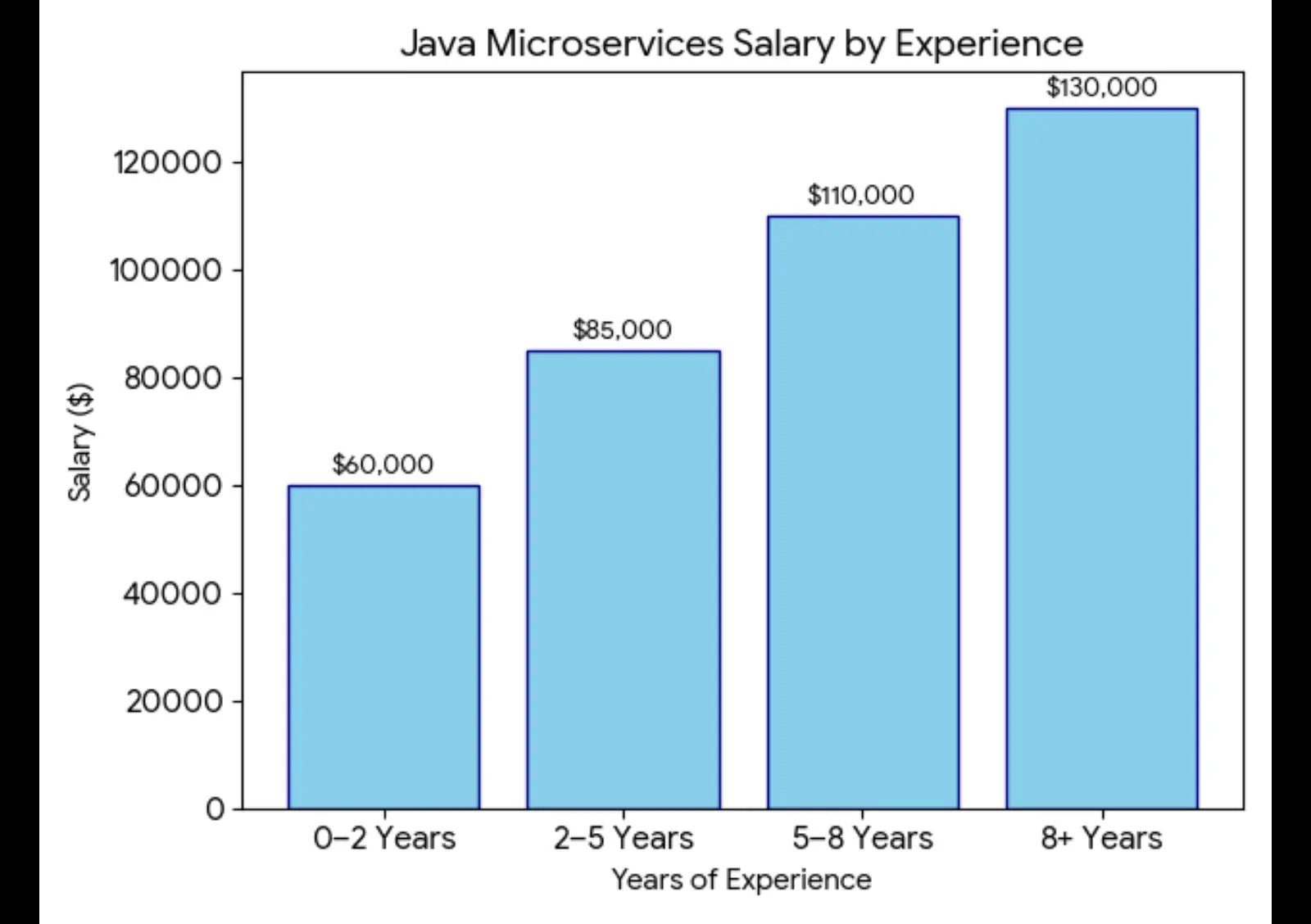
Entry-level positions can start around $60,000 - $85,000, while experienced professionals with 5+ years can command salaries well over $110,000, often reaching $1300,000+ for senior and lead roles.
Companies hiring Java Microservices professionals
Almost every major tech company and enterprise is adopting microservices, leading to a vast array of hiring opportunities. Some prominent companies actively hiring Java Microservices professionals include:
- Amazon
- Microsoft
- Netflix
- Facebook (Meta)
- IBM
- Oracle
- Salesforce
- Adobe
- Various FinTech companies (e.g., Stripe, PayPal)
- E-commerce giants
- Healthcare technology companies
And thousands of startups and mid-sized companies across every sector.
Roles and Responsibilities
A Java Microservices professional typically has a diverse set of responsibilities, including:
- Designing and Developing: Creating, building, and maintaining microservices using Java and Spring Boot.
- API Development: Designing and implementing robust RESTful APIs for service communication.
- Database Integration: Working with various database technologies (SQL and NoSQL) relevant to individual services.
- Cloud Deployment: Deploying and managing microservices on cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP).
- Containerization: Utilizing Docker to package and isolate microservices.
- Orchestration: Working with Kubernetes for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications.
- Testing: Writing unit, integration, and end-to-end tests for microservices.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing tools for tracking service performance and identifying issues.
- Security: Ensuring the security of microservices through authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
- Collaboration: Working closely with cross-functional teams, including product owners, architects, and DevOps engineers.
Steps to Prepare for Java Microservices Certification
While there isn't one official "Java Microservices Certification" from Oracle, several vendors offer certifications related to Spring, cloud platforms, and Kubernetes, which are highly relevant. Here's a general approach to prepare:
- Master Core Java: Ensure a strong foundation in Java SE concepts, including OOP, collections, multithreading, and exceptional handling.
- Learn Spring Framework: Deeply understand Spring Core, Spring MVC, and especially Spring Boot. Spring Boot is the de facto standard for building Java microservices.
- Explore Spring Cloud: This suite of tools is essential for building distributed systems with Spring. Focus on service discovery (Eureka), API Gateway (Zuul/Spring Cloud Gateway), load balancing (Ribbon), and circuit breakers (Hystrix/Resilience4j).
- Understand RESTful Principles: Be proficient in designing and consuming RESTful APIs.
- Database Knowledge: Gain experience with both relational (e.g., PostgreSQL, MySQL) and NoSQL (e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra) databases.
- Docker & Kubernetes: Learn how to containerize applications with Docker and orchestrate them using Kubernetes. This is critical for modern microservices deployment.
- Cloud Platforms: Get hands-on experience with at least one major cloud provider (AWS, Azure, or GCP) for deploying and managing microservices.
- Practice Projects: Build several end-to-end microservices projects from scratch to solidify your understanding.
- Consider Certifications: Look into certifications like:
-
-
Spring Certified Professional: Focuses on Spring Framework proficiency.
-
AWS Certified Developer - Associate / Solutions Architect - Associate: Validates cloud skills.
-
Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD) / Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA): Proves Kubernetes expertise.
-
Conclusion
Java Microservices offer a powerful and flexible approach to building modern applications, driving innovation and efficiency in the software industry. By investing in comprehensive training and continually honing your skills, you can unlock a wealth of career opportunities and become an indispensable asset to any forward-thinking organization. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards in terms of career growth, impactful work, and competitive compensation are well worth the effort. Start your Java Microservices journey today and build the future of software!
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

What Is Java Selenium? Beginner’s Guide to Automation Testing

Getting Started with Palo Alto Networks: Beginner’s Training Guide

.webp?width=1106&height=232&name=iteanz-java-microservices-training-cta%20(1).webp)
No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think